Contents:
- What is Outsourcing vs Offshoring
- Some key differences and real-life examples
- Conclusion
What is Outsourcing vs Offshoring:
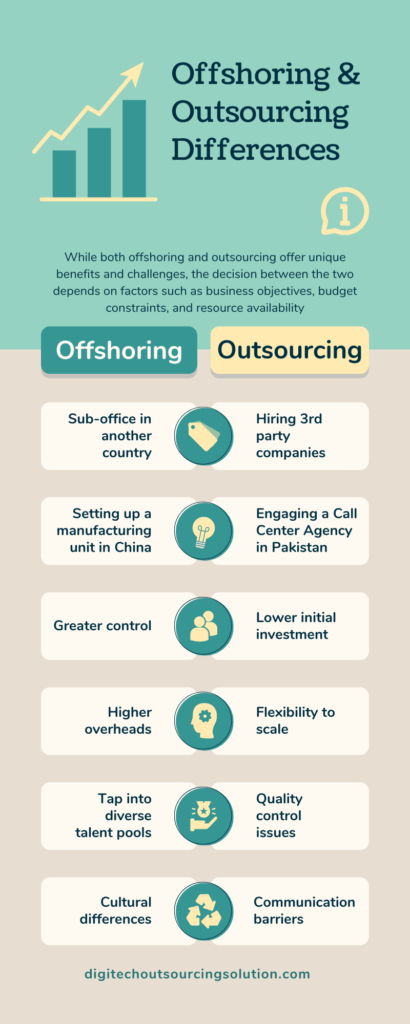
Outsourcing simply refers to hiring a third-party business to manage certain aspects of your business operation, while offshoring involves setting up your own business division in another country.
Outsourcing has become a prevalent business strategy across various industries, driven by the need for cost efficiency, flexibility, and access to specialized skills. By outsourcing non-core functions to third-party vendors or service providers, companies can focus on their core competencies and strategic objectives.
Offshoring, often used interchangeably with outsourcing, specifically refers to the relocation of business operations, functions, or processes to foreign countries. Unlike outsourcing, which can be domestic or international, offshoring involves the transfer of activities to offshore locations to capitalize on cost advantages, access to global talent, and other strategic benefits.
Definition:
| Aspect | Offshoring | Outsourcing |
| Definition | Setting up your own sub-office in another country | Hiring 3rd party companies in another country |
| Examples | Setting up a manufacturing unit in China | Engaging Call Center Agency without the need to manage the facility |
Benefits:
| Aspect | Offshoring | Outsourcing |
| Control | Greater control over processes and information | Lower initial investment and operational costs |
| Financial | Potential for long-term financial benefits | Access to specialized expertise and resources |
| Talent | Ability to tap into diverse talent pools and resources | Flexibility to scale operations up or down as needed |
| Business | To gain competitive edge with new geographies | To have more focus on core functions |
Risks:
| Aspect | Offshoring | Outsourcing |
| Investment | Higher initial capital investment and ongoing expenses | Quality control issues and dependency on external service providers |
| Management | Challenges in managing remote teams and cultural differences | Communication barriers and time zone differences |
| Security | Potential risks to data security and intellectual property | Concerns regarding confidentiality and data privacy |
Some Key Differences and Real-Life Examples
Examples of Outsourcing vs Offshoring:
If you lack the necessary expertise to develop and maintain a website or operate a call center, you may choose to outsource these tasks to a specialized IT or call center service provider in another country.
Outsourcing can range from simple tasks, such as hiring a virtual assistant from countries like Pakistan or the Philippines, to more complex arrangements, such as contracting with a call center equipped with 100 seats to handle nationwide phone answering services for your business.
Additionally, you might decide to outsource the manufacturing of a white-label product intended for sale on Amazon, contracting with a manufacturer to produce the product on your behalf.
An example of offshoring involves establishing a manufacturing unit in a foreign location like Shenzhen while retaining management control. Offshoring entails a more intricate process compared to outsourcing, due to the significant initial investment and ongoing management requirements associated with operating a foreign office
Conclusion:
Both offshoring and outsourcing play crucial roles in today’s global economy, offering businesses opportunities to optimize operations, access new markets, and drive growth. By understanding the differences between the two approaches and carefully evaluating their benefits and risks, businesses can make informed decisions to achieve their strategic objectives and remain competitive in the marketplace.
You can read more about Business Outsourcing in this article




